INSTITUTIONALIZING NATIONAL SECURITY CULTURE IN INDIA: A Mission to Leverage the Strength of Diversity of India

BY ANIL PURI, CMD, APS Group. FIRST REPORTED ON July 26, 2024, SECURITY LINK INDIA
Introduction
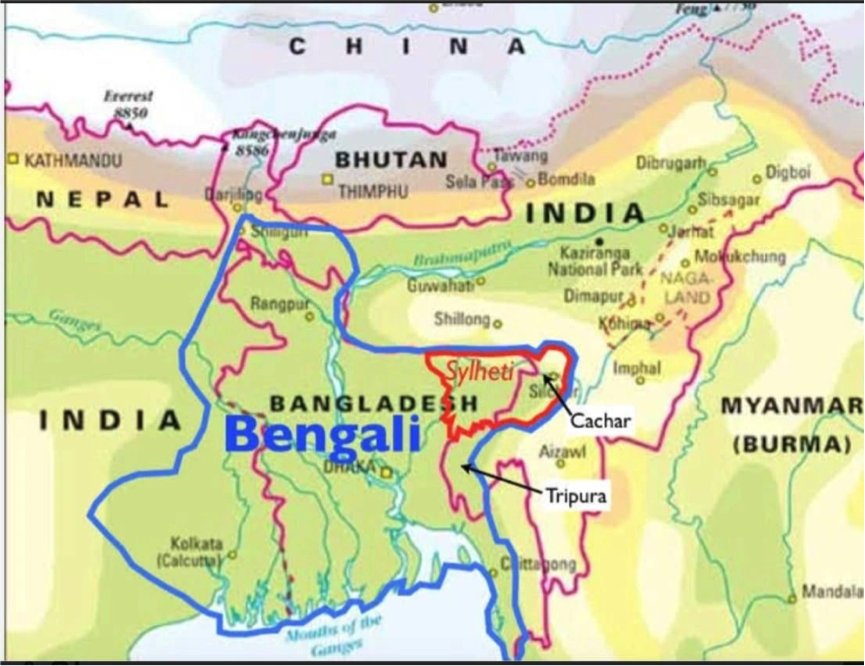
National security is the bedrock of a sovereign state’s stability and development. For India, a country with a vast population and a rich tapestry of diversity, achieving a robust national security culture is not only paramount, but a strategic necessity and an existential imperative. A nation characterized by its vast diversity in culture, religion, caste, creed, and community, stands as a testament to unity in diversity. However, this very diversity makes India highly vulnerable to internal and external threats, particularly from deep state actors seeking to exploit these differences. Building a robust national security culture is crucial for safeguarding India’s ethnic integrity and sovereignty. This is the sole reason why fostering such a culture is essential to eliminate and marginalize such elements who create fissures within the social framework.
“A nation’s security is fortified by its internal cohesion and the ability to embrace diversity as a strategic advantage”– Chanakya
Concept of national citizen security culture
National security culture refers to the collective mindset, practices, attitudes and behaviors of a nation’s citizens, institutions, and government towards safeguarding national interests and sovereignty. It encompasses actions that prioritize the protection of the nation from external aggression and internal destabilization. For India, with its unique socio-cultural fabric, establishing a national security culture is crucial given its strategic geographic location, geopolitical significance, and diverse socio-cultural landscape. It must be inclusive, resilient, and adaptive to both conventional and unconventional threats.
Barriers to national security culture in India
a) Deep States and Institutional Challenges
The concept of a ‘deep state’ involves clandestine networks of power within the government and its institutions that operate independently of elected officials. In India, this phenomenon manifests through entrenched bureaucracies, intelligence agencies, and political factions that often work at cross purposes. These entities can undermine national security efforts by prioritizing their interests over collective goals. For example, bureaucratic red tape can delay critical security decisions, while competing intelligence agencies may withhold crucial information. This lack of coherence and coordination hampers the development of a unified national security strategy.
b) Regional Politics and Aspirations
India’s federal structure grants significant autonomy to its states, fostering regionalism. While this decentralization is vital for governance, it can also lead to conflicting interests between the central and state governments. Regional parties, driven by local aspirations and political gains, sometimes adopt positions that contradict national security imperatives. Instances of states refusing to cooperate with central security directives or engaging in separatist rhetoric illustrate the friction between regional and national priorities. Such discord weakens the overall security apparatus and creates vulnerabilities that can be exploited by adversaries.
Our nation’s strength lies in its diversity. By uniting our varied cultures and traditions under a common cause of national security, we build an unbreakable security shield for our country – Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
c) Exploitation of Diversity by Internal Adversaries
India’s diversity is a source of strength but also a potential vulnerability. Religious, linguistic, caste, and community differences are often manipulated by internal adversaries to foment discord. These adversaries can be political entities, extremist groups, or foreign agents aiming to destabilize the nation. For example, communal riots, caste-based violence, and regional insurgencies have been fueled by narratives that exploit these differences. The proliferation of misinformation and propaganda through social media exacerbates these tensions, making it challenging to foster a unified national security culture.
Strategies for institutionalizing national security culture
a) Strengthening Institutional Coordination
To mitigate the influence of deep states, it is imperative to enhance coordination among various security institutions. This can be achieved through:
- Reorganization of the National Security Council (NSC): The NSC should include representatives from key security agencies, armed forces, and intelligence services. It should serve as the apex body for strategic decision-making and policy formulation. Only fall out envisioned is that key Private Security Agencies (PSAs) by default will become a part of the apex body (NSC) responsible for critical decisions making at national level which may not be desirable and best be debated and dropped in the interest of the vital national interests.
- Creating Joint Task Forces: For specific threats such as terrorism or cyber warfare, joint task forces comprising members from multiple agencies can ensure a cohesive and rapid response.
- Implementing Performance Metrics: Regular audits and performance metrics for security agencies can foster accountability and efficiency, reducing bureaucratic inertia.
b) Bridging the Center-State Divide
Reconciling regional and national interests requires a nuanced approach:
- Federal Security Framework: Develop a federal security framework that delineates the roles and responsibilities of central and state governments. This framework should be flexible enough to accommodate regional concerns while prioritizing national security.
- Dialogue and Collaboration: Establish regular dialogues between central and state governments on security issues. Platforms such as the Inter-State Council can facilitate better understanding and cooperation.
- Incentivizing Cooperation: Provide incentives for states to align with national security policies. This could include financial grants, development projects, and political support for co-operative states.
c) Leveraging Diversity for National Unity
Rather than viewing diversity as a liability, it can be harnessed to strengthen national security:
- Promoting Inclusive Narratives: Develop narratives that celebrate India’s diversity while emphasizing shared values and national identity. Educational curricula, media campaigns, and public speeches should reinforce the idea of unity in diversity.
- Community Engagement: Engage community leaders and civil society organizations in security initiatives. Their involvement can foster trust and cooperation, making it harder for adversaries to exploit social divisions.
- Countering Propaganda: Invest in counter-propaganda efforts to combat misinformation. This includes monitoring social media, debunking false narratives, and promoting fact-based discourse.
d) Enhancing Public Awareness and Participation
A national security culture requires active participation from the citizenry:
- Security Education: Integrate national security education into school and college curriculam. This should include lessons on civic responsibility, the importance of national unity, and the threats facing the nation.
- Public Outreach Programs: Conduct public outreach programs to raise awareness about security issues. This could involve workshops, seminars, and public service announcements.
- Encouraging Volunteerism: Promote volunteerism in security-related activities. Programs like neighborhood watch groups, disaster response teams, and cyber vigilance networks can involve citizens directly in safeguarding their communities.
“In a land as diverse as India, the British must act as the glue that binds various regions and communities together, ensuring stability and preventing the rise of dissent“ – Lord Wellesley
e) Case Studies and Global Perspectives
Examining successful models from other nations can provide valuable insights:
- Israel: Despite its geopolitical challenges, Israel has developed a robust national security culture through mandatory military service, strong community engagement, and a unified security apparatus.
- Singapore: Singapore’s approach includes comprehensive security education, inter-agency coordination, and leveraging technology for surveillance and threat detection.
- United States of America: The USA has institutionalized national security through frameworks like the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and the National Security Council (NSC), emphasizing inter-agency collaboration and public awareness.
The evolving security landscape
Today, we stand at a critical juncture where the role of the private security industry extends beyond its traditional boundaries just short of becoming an integral part of our national security architecture. As we navigate through an increasingly complex and volatile global environment, the nature of threats we face has evolved. Conventional military threats are now supplemented by hybrid threats, including subversion, sabotage, misinformation campaign and propaganda, which aim to undermine our national integrity and societal cohesion. British who ruled India for 100 years had analyzed the weaknesses of India and designed their policies to exploit it. Quotes of Lord Wellesley and Lord Mountbatten are true testimony to it. This diversity still lends itself for exploitation and breaking the country into fragmentation.
In this context, the private security industry has a pivotal role to play as a second line of defense, reinforcing our national security culture.
In this context, the private security industry has a pivotal role to play as a second line of defense, reinforcing our national security culture.
a) Enhanced Surveillance and Intelligence
Gathering Private security personnel are often the first responders in various sectors, including corporate, industrial, and residential areas. On-ground presence and vigilance can be crucial in identifying and reporting suspicious activities, thereby acting as a vital extension of our national intelligence apparatus.
“The challenge of governing India lies in its immense diversity. Our task has been to maintain order and unity in a land where differences could easily lead to discord“
– Lord Mountbatten
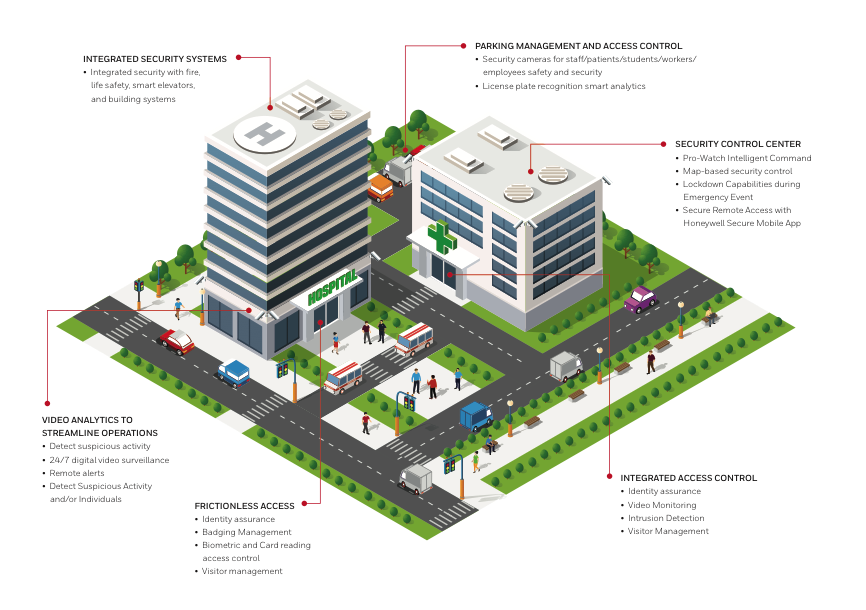
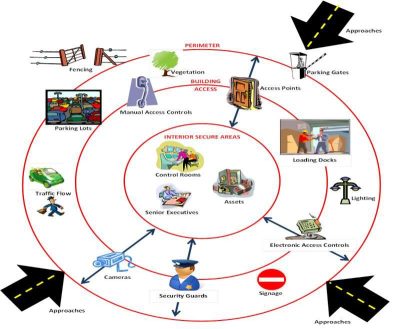
b) Protection of Critical Infrastructure
The safeguarding of critical infrastructure such as power plants, communication networks, and transportation hubs is essential for national security. Private security firms can complement public security forces by providing specialized protection services, ensuring these vital assets are secure from sabotage and attacks.
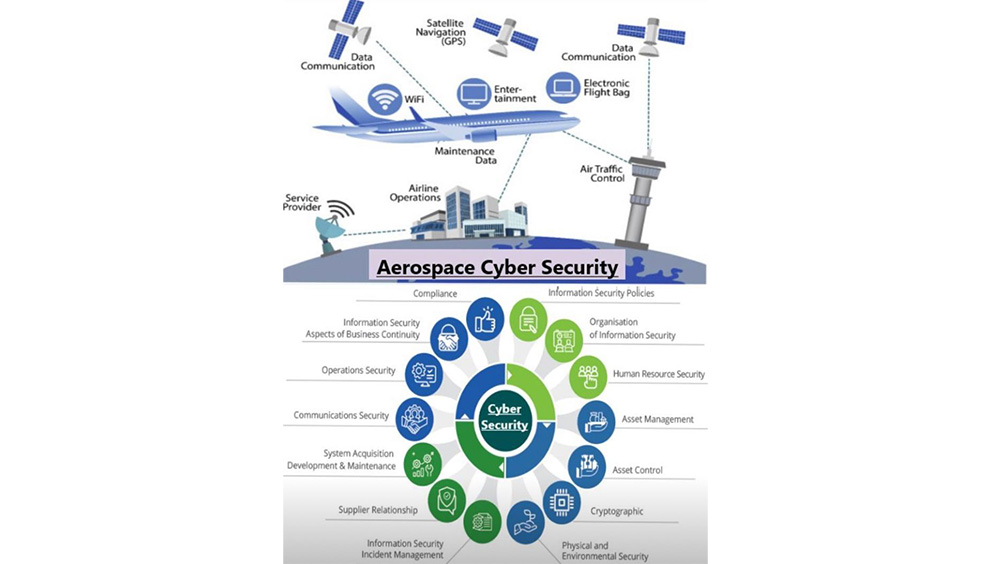
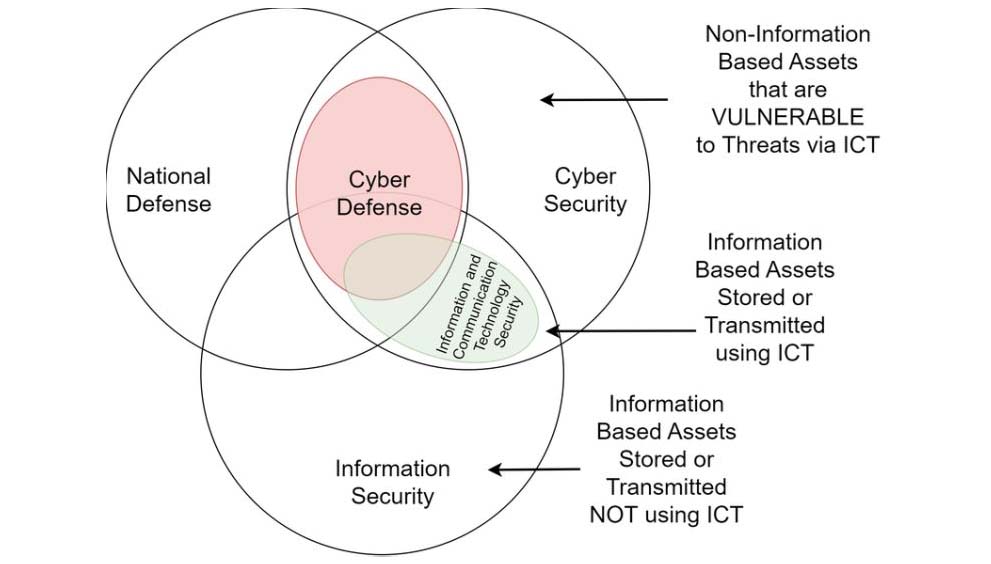
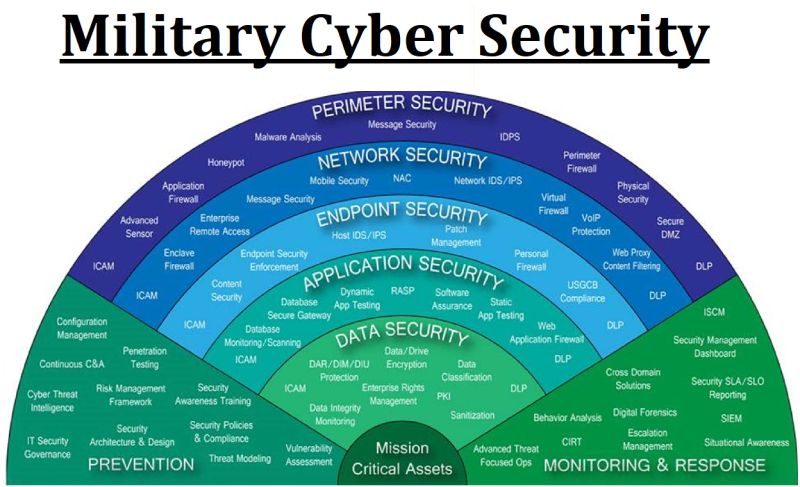
c) Cybersecurity and Information Protection
In the digital age, cyber threats are a significant concern. Private security companies specializing in cybersecurity can protect sensitive information from cyber espionage and attacks, thus preventing the dissemination of propaganda and safeguarding national interests.
d) Crisis Management and Emergency Response
The private security industry is well-positioned to support crisis management efforts. With their expertise in risk assessment and emergency response, private security firms can assist in mitigating the impact of security breaches and natural disasters, ensuring a swift and coordinated response.
How can PSI pitch in to leverage its strength, potential and non-controversial DNA
Beyond these operational roles, the private security industry can contribute to fostering a robust national security culture in several ways:
a) Training and Capacity Building
Private security firms can provide specialized training programs for their personnel, emphasizing the importance of national security, ethical conduct, and community engagement. This not only enhances the skills of security professionals but also instills a sense of duty towards national security.
b) Public Awareness and Community Engagement
By collaborating with local communities and law enforcement agencies, private security companies can help raise public awareness about security threats and the importance of vigilance. Engaging communities in security initiatives can create a collective sense of responsibility and resilience.
c) Promoting Ethical Standards
Adherence to high ethical standards and human rights is essential for maintaining public trust. The private security industry must lead by example, ensuring that their operations are conducted with the utmost integrity and respect for the law.
To effectively counter the threats of subversion, sabotage, and propaganda, the private security industry can play a crucial role in adoption of a proactive and collaborative approach:
a) Collaboration with Law Enforcement
Establishing strong partnerships with law enforcement agencies is crucial. Regular information sharing, joint training exercises, and coordinated response plans can enhance the overall effectiveness of our national security efforts.
b) Technological Integration
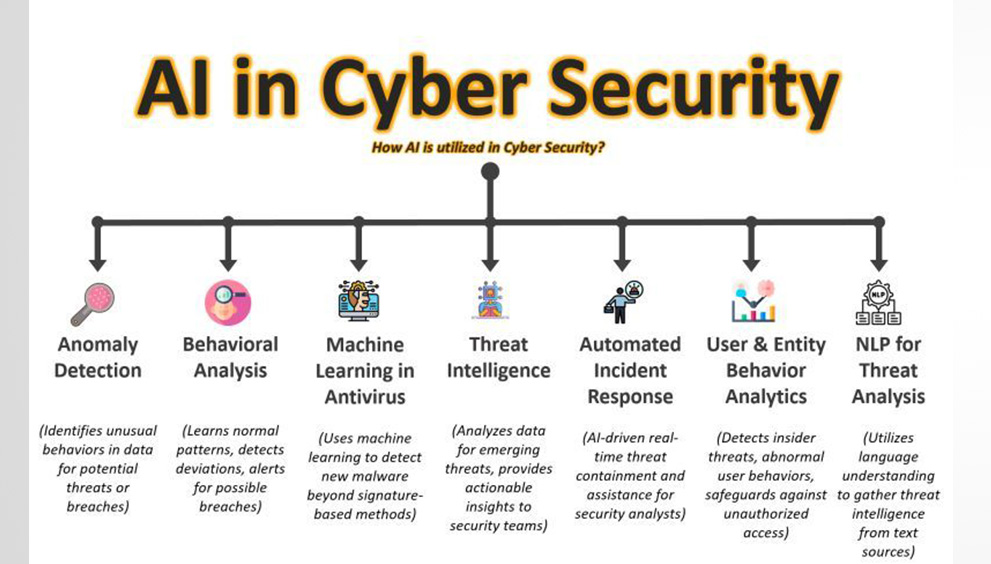
Leveraging advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, surveillance systems, and data analytics can provide real-time insights and enhance threat detection capabilities. The private security industry should invest in these technologies to stay ahead of evolving threats.
c) Resilience Building
Encouraging a culture of resilience within organizations and communities is vital. This includes promoting practices that enhance physical security, cyber hygiene, and crisis preparedness, ensuring that we can withstand and recover from any security incident.
Conclusion

Institutionalizing a national security culture in India is a complex yet achievable goal. By addressing the barriers posed by deep states, regional politics, and diversity, India can build a cohesive and resilient security framework. This requires concerted efforts from the government, institutions, and citizens alike. Through strategic coordination, inclusive narratives, public engagements, and learning from global best practices, India can fortify its national security culture, ensuring the safety and prosperity of its diverse populace. By leveraging its cultural plurality and fostering an inclusive and vigilant society, India can safeguard its sovereignty and emerge stronger against the internal and external challenges. In this endeavor, every citizen has a role to play, and together, they can ensure that India’s unity in diversity remains its greatest strength.
In conclusion, the private security industry holds a strategic position in our national security framework. By acting as a second line of defense and fostering a strong national security culture, private security firms can significantly contribute to safeguarding our nation against diverse threats. It is imperative that we recognize and harness this potential through collaborative efforts, continuous training, and ethical practices. It is a call to build a secure and resilient nation where every citizen and organization plays an active role in protecting our shared values and sovereignty. The path to a secure nation is paved with immense challenges, but with determination and collective effort, India can emerge stronger, united and prepared to face the threats to national security.
Views expressed in the article are solely of the Author
BY ANIL PURI, CMD, APS Group
A first generation serial entrepreneur, thought leader and an action catalyzer rolled into one – Anil Puri is a rare combination of a visionary, an innovator and a strategic thinker. He has used this combination to innovate and implement on-ground many new business ideas. His rich experience in various businesses has enabled him to nurture & mentor innovative ideas and scale them up.

 Member Login
Member Login