Ai In Advanced Security Systems

By Soumyaranjan Das
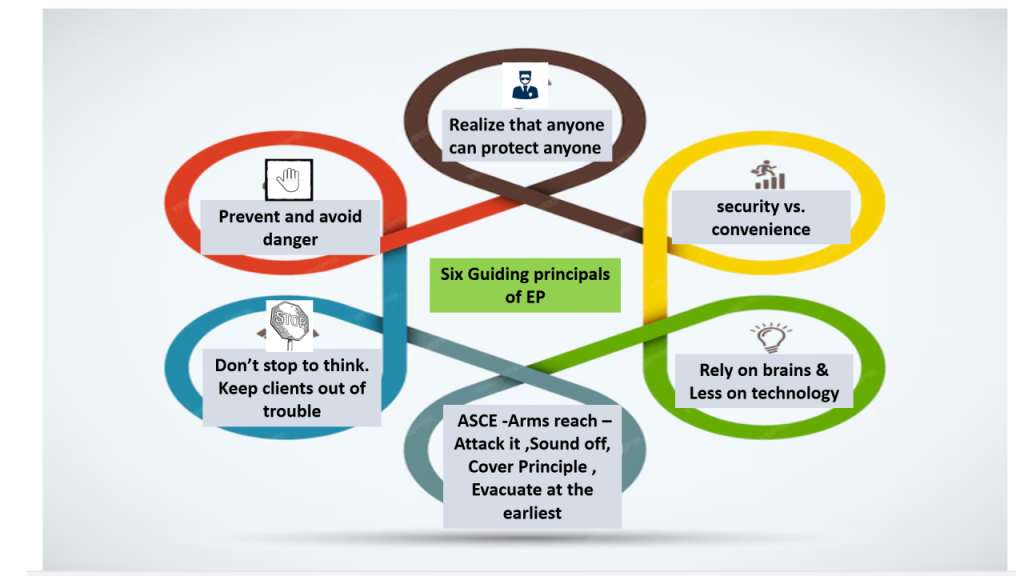
AI is implemented in advanced security systems in many ways to enhance their effectiveness and efficiency. Here are some common use cases.
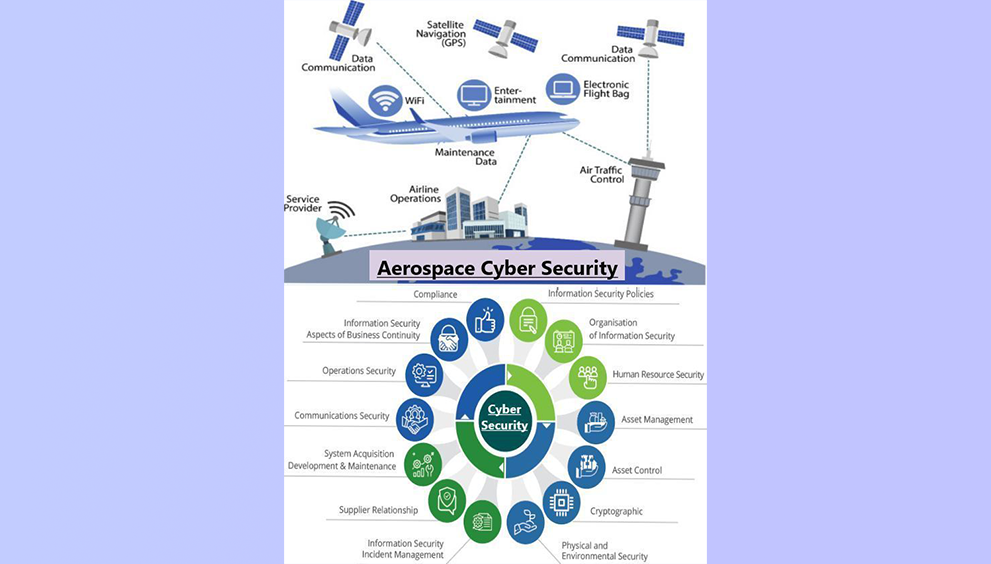
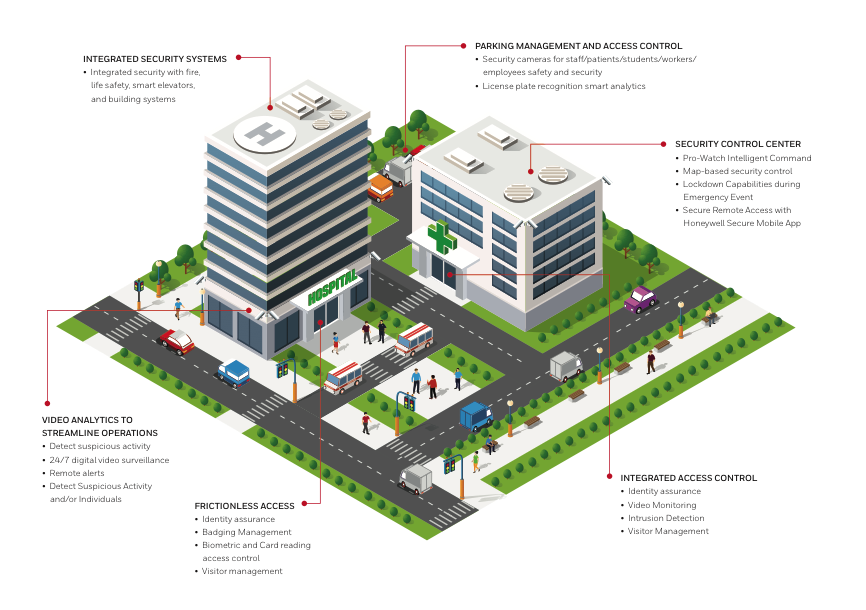
- Facial Recognition: AI is used to identify and verify individuals by analyzing facial features. This technology is used for access control, surveillance, and authentication.
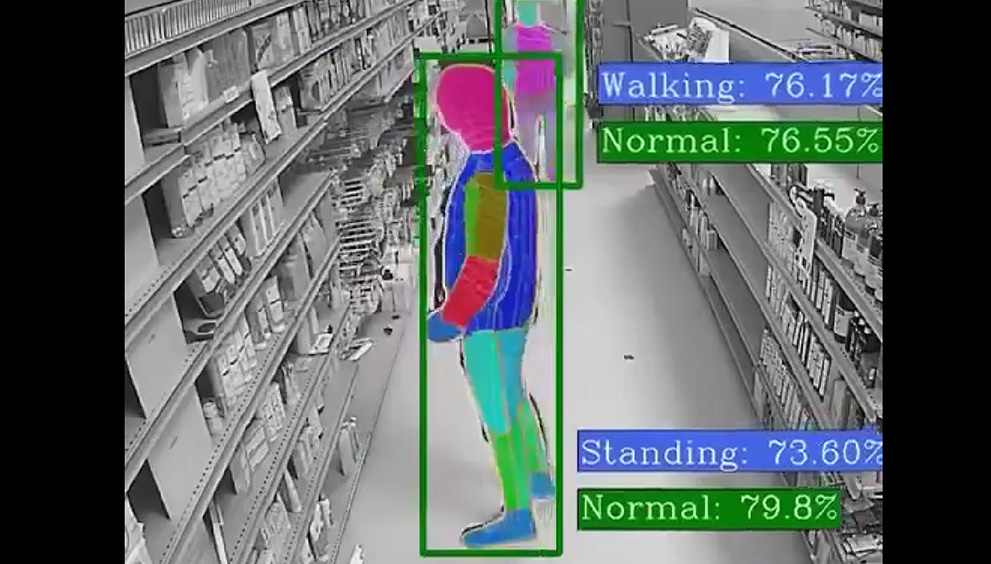
- Behavioral Analysis: AI algorithms can analyze human behavior patterns to detect suspicious or abnormal activities. This is particularly useful in video surveillance systems.
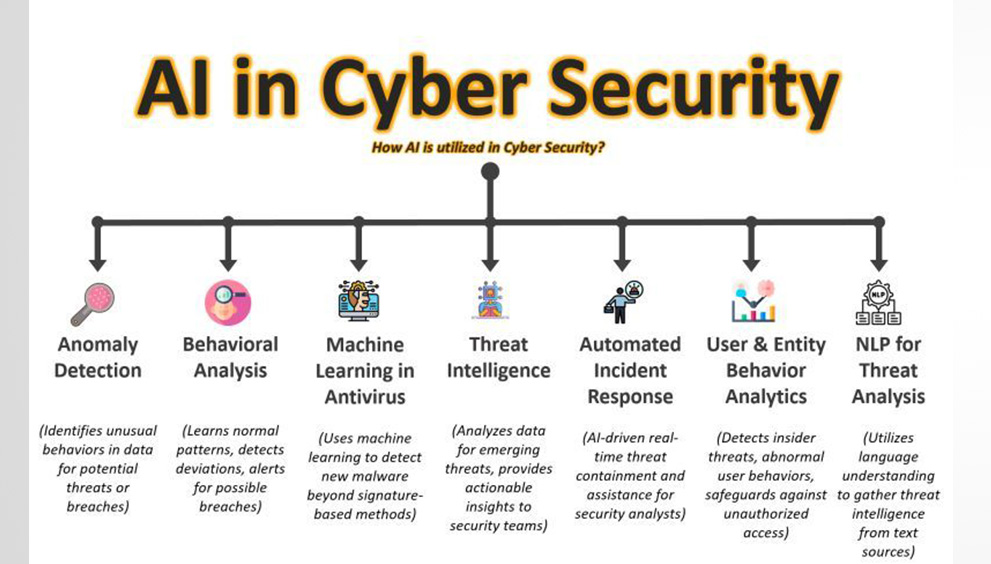
- Anomaly Detection: AI can learn what normal network traffic looks like and detect anomalies that may indicate a security breach or attack.
- Threat Intelligence: AI can analyze large volumes of data to identify potential security threats and help security teams respond more effectively.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can predict potential security threats based on historical data and trends, enabling proactive security measures.

- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP can be used to analyze text data, such as emails or chat logs, to detect phishing attempts or other malicious activities.
- Automation: AI can automate routine security tasks, such as patch management and vulnerability scanning, to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of human error.
- Machine Learning in Antivirus Software: Machine-learning algorithms can improve the accuracy of antivirus software by identifying new malware based on patterns and behavior.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can analyze data from security equipment such as cameras and sensors to predict when maintenance is needed, reducing downtime and ensuring optimal performance.
- Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR): AI can be used to automate incident response processes, including alert triage, investigation, and remediation, helping security teams respond to threats more quickly and effectively.
- IoT Security: AI can analyze data from IoT devices to detect anomalies and potential security breaches, helping to secure networks and protect sensitive information.
- Fraud Detection: AI can analyze transaction data to detect patterns indicative of fraud, helping financial institutions and businesses prevent fraudulent activities.
- Cyber Threat Hunting: AI can assist security analysts in proactively searching for and identifying cyber threats within an organization’s network.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): AI can analyze user and entity behavior to detect suspicious activities and insider threats.

- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): AI can enhance SIEM systems by improving log analysis, correlation, and alerting capabilities, helping to identify and respond to security incidents more effectively.
- Virtual Security Analysts: AI-powered virtual analysts can assist human analysts by performing tasks such as data correlation, threat intelligence gathering, and incident investigation.
- Biometric Security: AI can enhance biometric authentication systems by improving accuracy and security, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Network Security: AI can be used to monitor network traffic and detect and respond to potential threats, such as malware, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access attempts.
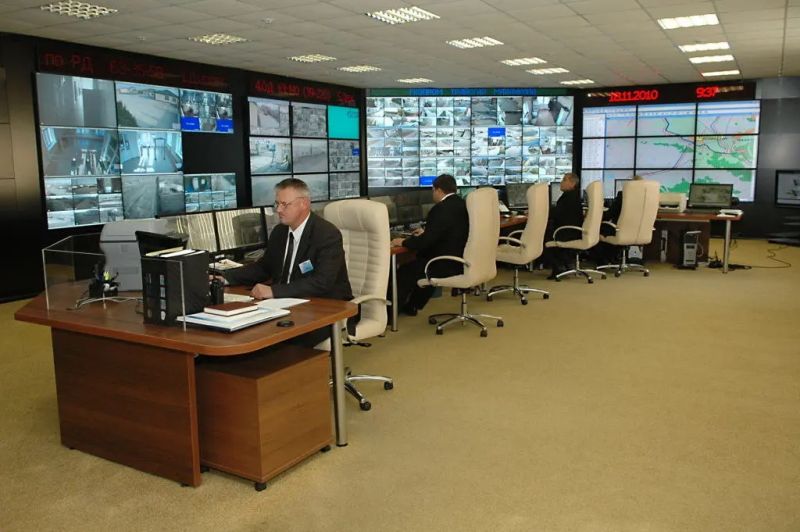
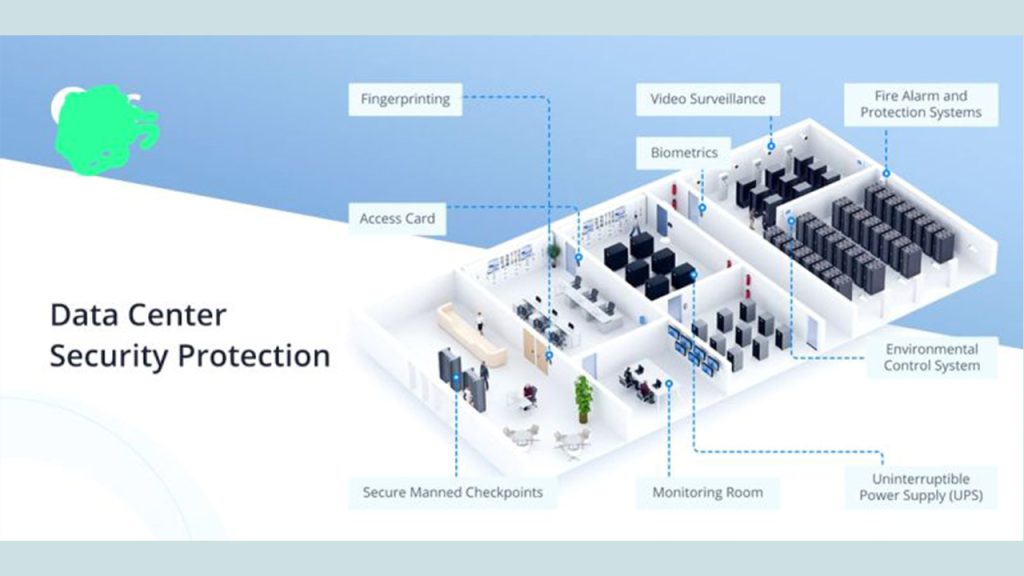
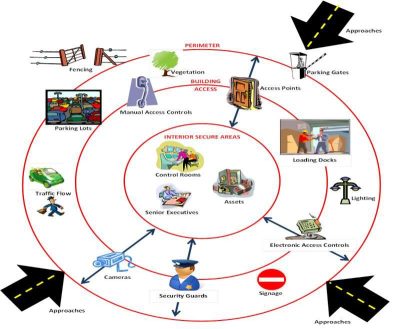
- Physical Security: AI can enhance physical security systems, such as access control systems and surveillance cameras, by enabling features like facial recognition, object detection, and real-time threat detection.
- Cyber-security Forensics: AI can assist in digital forensic investigations by analyzing large volumes of data to identify the source and impact of security breaches.
- Supply Chain Security: AI can be used to monitor and secure supply chains by analyzing data to detect anomalies or potential threats to the integrity of the supply chain.
- Cloud Security: AI can help secure cloud environments by monitoring for unauthorized access, detecting and responding to anomalies, and improving overall security posture.
- Endpoint Security: AI-powered endpoint security solutions can detect and respond to threats on individual devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and IoT devices
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: AI can facilitate the sharing of threat intelligence between organizations, helping to improve overall cybers-ecurity defenses.
- Security Compliance: AI can assist organizations in maintaining compliance with security regulations and standards by automating compliance monitoring and reporting.
- Dynamic Threat Response: AI can analyze real-time security data to dynamically adjust security measures, such as firewall rules and access controls, in response to emerging threats.
- Ransomware Protection: AI can help protect against ransomware attacks by detecting suspicious file behavior and preventing unauthorized file encryption.
- Social Engineering Detection: AI can analyze communication patterns and content to detect social engineering attacks, such as phishing and pretexting.
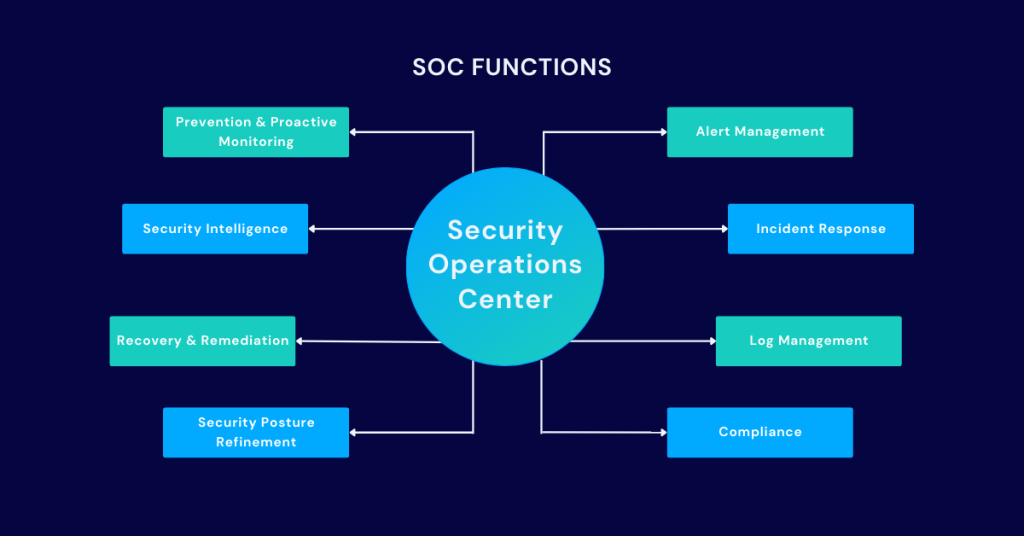
- Security Operations Center (SOC) Optimization: AI can optimize SOC operations by automating repetitive tasks, correlating security events, and prioritizing alerts for analysts.
- Vulnerability Management: AI can assist in identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities in systems and applications, helping organizations patch and mitigate risks more efficiently.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): AI can enhance IAM systems by analyzing user behavior and access patterns to detect and prevent unauthorized access attempts.
- Security Automation: AI can automate security processes such as incident response, threat hunting, and security policy enforcement, improving efficiency and reducing human error.
- Blockchain Security: AI can enhance the security of blockchain networks by detecting and responding to suspicious transactions and activities
- Physical Access Control: AI can enhance physical access control systems by integrating with biometric authentication methods and analyzing access patterns to detect anomalies.
- Secure Software Development: AI can help developers write more secure code by identifying and fixing vulnerabilities early in the development process.
- Deepfake Detection: AI can be used to detect and mitigate the threat of deepfake videos and images, which can be used to spread misinformation or impersonate individuals.
- Security Policy Management: AI can assist in managing and enforcing security policies across an organization’s IT infrastructure, ensuring compliance and consistency.
- Incident Response Automation: AI can automate parts of the incident response process, such as containment and remediation, to reduce response times and limit the impact of security incidents.
- Secure Authentication: AI can improve the security of authentication methods, such as password-based authentication, by analyzing user behavior and detecting anomalies.
- Cloud Workload Protection: AI can help protect cloud workloads by analyzing network traffic and behavior patterns to detect and respond to threats.
- Cyber Threat Intelligence Analysis: AI can analyze cyber threat intelligence data to identify emerging threats and help organizations prepare and respond accordingly.
- Physical Threat Detection: AI can analyze video feeds from surveillance cameras to detect physical threats, such as intruders or suspicious packages.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): AI can help prevent data loss by analyzing data access patterns and detecting and responding to unauthorized attempts to access or exfiltrate data.
- Supply Chain Risk Management: AI can analyze supply chain data to identify and mitigate security risks, such as counterfeit components or supplier vulnerabilities.
- Security Training and Awareness: AI can be used to develop personalized security training programs for employees based on their roles and behavior patterns.
- Fraud Prevention in Banking: AI can analyze banking transactions in real-time to detect and prevent fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized transactions or identity theft.
- Insider Threat Detection: AI can analyze user behavior and access patterns to identify potential insider threats, such as employees accessing sensitive information without authorization.
- Secure Data Sharing: AI can facilitate secure data sharing between organizations by encrypting data, enforcing access controls, and monitoring data usage.
- Security Assessment and Auditing: AI can assist in conducting security assessments and audits by analyzing system configurations, logs, and network traffic to identify vulnerabilities and compliance issues.
- Autonomous Security Systems: AI can enable autonomous security systems that can detect, analyze, and respond to security threats without human intervention.
- Safety and Security in Autonomous Vehicles: AI can enhance the safety and security of autonomous vehicles by detecting and responding to potential threats, such as collisions or hacking attempts.
- Secure Internet of Things (IoT) Devices: AI can help secure IoT devices by monitoring device behavior, detecting anomalies, and mitigating security risks.
- Security in Smart Cities: AI can enhance security in smart cities by analyzing data from various sensors and devices to detect and respond to security threats, such as traffic congestion or public safety incidents.
- Biometric Authentication for Physical Access: AI can improve biometric authentication systems for physical access control by enhancing accuracy and detecting spoofing attempts.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: AI can assist in disaster recovery and business continuity planning by analyzing risks, prioritizing recovery efforts, and automating recovery processes.
- These applications highlight the broad range of ways in which AI is being used to enhance security across different sectors and technologies.
By Soumyaranjan Das

 Member Login
Member Login